In early April 2025, the U.S. stock market experienced a significant crash, primarily triggered by the implementation of aggressive tariff policies by President Donald Trump. This event, referred to as “Liberation Day,” led to substantial market losses and raised concerns about a potential recession.
Over a span of just 32 trading sessions, the Nasdaq Composite Index plummeted from 20,204 to 17,398, marking a substantial 14% decline and officially entering bear market territory—a status defined by a 20% drop from recent highs. This downturn wasn’t isolated; the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 also experienced significant pullbacks. Concurrently, the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as the market’s “fear gauge,” surged to 45.3, its highest level since April 2020 when the COVID-19 pandemic first unsettled global markets.
In total, the U.S. stock market shed over $6 trillion in value within just two days, representing one of the swiftest and most substantial market wipeouts since the dot-com bubble burst.
What Caused the 2025 Market Crash?
The Tariff Shock on “Liberation Day”
The primary catalyst behind this abrupt market downturn was the announcement of extensive tariff hikes by President Donald Trump. On April 2, 2025, dubbed “Liberation Day,” the administration imposed a baseline 10% tariff on all imports, with significantly higher rates targeting specific countries. Notably, tariffs on Chinese goods escalated to 54%, marking the highest levels in over a century.

These aggressive trade policies ignited fears of a global trade war, leading to increased costs for companies reliant on imports, disruptions in supply chains—especially in industries like technology and automotive—and heightened concerns about an impending recession. The combination of these factors contributed to the rapid and severe decline observed in the stock markets.
Sources: AP News
| Country | Tariff Rate Imposed by U.S. |
| China | 54% |
| European Union | 20% |
| Vietnam | 46% |
| Thailand | 36% |
| Japan | 24% |
| Cambodia | 49% |
| Taiwan | 32% |
These tariffs were justified by the administration as measures to address trade imbalances and protect domestic industries. However, they were met with immediate retaliatory actions from affected nations, notably China, which imposed a 34% tariff on U.S. goods, amplifying market anxieties.
Sources: The Guardian
The Immediate Market Impact
The fallout from the policy was swift and brutal—sending shockwaves through major U.S. indices and beyond:
- April 3, 2025:
| Index | % Change (April 3, 2025) |
| S&P 500 | -4.8% |
| Nasdaq Composite | -5.9% |
| Dow Jones Industrial Average | -4.0% |
| DJIA Point Loss (48 hrs) | -4,000 pts |
| VIX | 45.3 |
These declines represented some of the most significant single-day losses since the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic-induced market downturn.
The volatility continued over the following days, with the DJIA losing a total of 4,000 points within 48 hours, marking the first back-to-back 1,500+ point losses in its history. The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as the “fear index,” surged to its highest level since 2020.
Economic Repercussions
But the stock tickers don’t tell the full story. The broader economic consequences are now coming into sharper focus.
The tariff implementations and ensuing market instability raised fears of an impending recession. BlackRock CEO Larry Fink indicated that the U.S. might already be in a recession, with potential for further market declines. Similarly, Bill Ackman described the tariff measures as an “economic nuclear war,” advocating for a 90-day pause to facilitate negotiations.
Source: Business Insider
Economists cautioned that:
- Inflation would rise due to higher import costs
- Growth would slow dramatically
- Stagflation—a toxic mix of high inflation and stagnating growth—was a rising concern
Source: US News
Business Impacts:
- Higher Costs: Businesses reliant on imports, particularly in the tech and retail sectors, faced increased input costs.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Industries such as electronics and automotive, which depend heavily on Chinese components, encountered significant operational challenges.
- Slower Growth: The tariffs dampened trade and demand, intensifying existing recession concerns within the U.S. economy.
- Inflation vs. Growth Dilemma: Elevated import costs led to higher consumer prices, while weakened demand threatened economic growth, placing the Federal Reserve in a precarious position.
Nasdaq’s Entry into Bear Market Territory
The Nasdaq’s fall from 20,204 to 17,398 over just 32 sessions places it among the fastest bear market transitions since 2000.
A bear market is characterized by a decline of 20% or more from recent highs. Despite the correction, valuations remained elevated:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio:
- At Peak: 38x
- Post-Correction: 30x Forbes
- Long-Term Average: 25x
This indicates that, even after significant losses, the market was not necessarily undervalued, especially considering potential earnings impacts in a recessionary environment.
The Big Tech Conundrum
The so-called “Magnificent Seven” tech giants bore the brunt of the market meltdown:
- Nvidia: Shares fell approximately 30% in 2025.
- Tesla: Experienced a 43% decline.
- Apple: Saw a 27% drop. Business Insider
- Alphabet (Google): Decreased by 23%.
- Amazon: Fell 21%. The Guardian+1Forbes+1
- Microsoft: Down 16%. The Guardian+1Business Insider+1
- Meta Platforms: Declined 14%. Business Insider
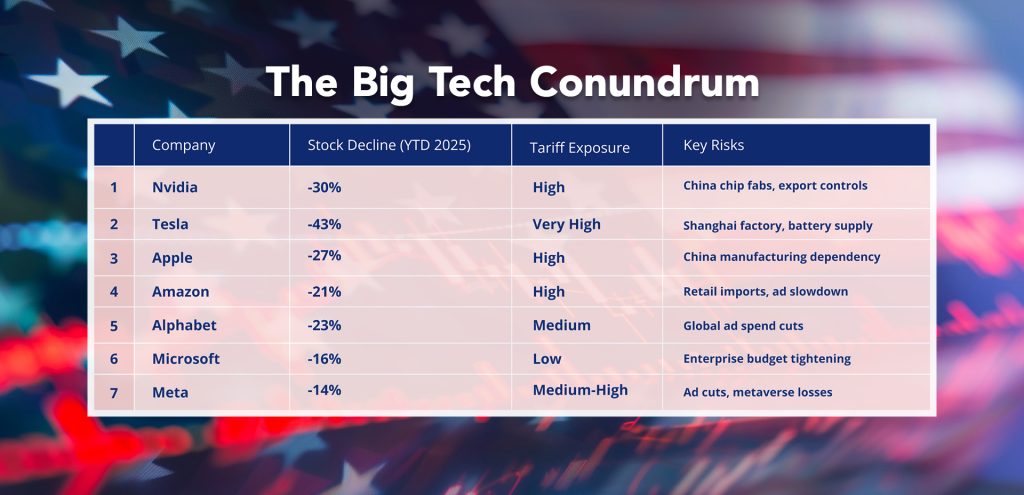
The extent of these losses was influenced by each company’s exposure to tariffs and global supply chains:
- Apple: Heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing, facing potential margin compression and reduced demand due to increased product prices.
- Tesla: Vulnerable due to its Shanghai Gigafactory and dependence on Chinese components like batteries and chips.
- Amazon: Confronted with higher retail prices from imports and a slowdown in global ad spending, impacting its revenue streams.
Even companies with lower direct exposure, such as Microsoft and Alphabet, faced risks from reduced enterprise spending and global advertising cuts, respectively.
Echoes of 1987’s Black Monday and COVID-19
The 2025 crash has drawn comparisons to previous downturns:
- The rapidity and severity of the 2025 crash drew comparisons to the infamous Black Monday of 1987.
On October 19, 1987, the DJIA experienced a record-breaking one-day decline of 22.6%, a day that became known as Black Monday. The crash was attributed to factors such as overvalued stocks, computerized trading programs, and investor panic. Despite the severity of the drop, the market recovered relatively quickly, with the DJIA regaining its pre-crash levels within two years.
2. April 2025’s market crash also drew comparisons to COVID-19 market crash.
In March 2020, the stock market experienced a rapid decline as the COVID-19 pandemic led to global economic shutdowns. The S&P 500 dropped approximately 34% from its February highs to its March lows. However, aggressive fiscal and monetary policies facilitated a swift recovery, with the market reaching new highs by the end of the year.
In both cases, sudden policy shifts and global fear fueled massive sell-offs—just as we’re seeing in 2025.

Global Response and Ongoing Developments
To ease tensions, the European Union proposed a “zero-for-zero” tariff agreement to eliminate tariffs on industrial goods, aiming to de-escalate the situation. However, the U.S. administration responded that the EU must also reduce non-tariff barriers, such as value-added taxes and stringent regulations, for negotiations to proceed. The Irish Sun
As of April 8, 2025, President Trump showed no indication of pausing or reversing the tariff measures, stating that the U.S. was not considering a pause in tariffs. This stance suggests that market volatility may persist, with ongoing risks of a global trade war and further economic downturn. The Guardian
The 2025 U.S. stock market crash was precipitated by aggressive tariff policies leading to significant market losses and heightened fears of a recession. The situation remains fluid, with potential for further economic implications depending on policy decisions and international responses in the coming weeks.
Impact on eCommerce Industry
The newly imposed tariffs have profound implications for the eCommerce sector, affecting both operations and consumer behavior.
Increased Operational Costs
eCommerce businesses, particularly those reliant on imported goods, are facing higher procurement costs due to the tariffs. For instance, imports from China are now subject to a cumulative tariff rate of 54%, significantly increasing the cost of products sourced from this region. These increased costs may compel online retailers to raise prices, potentially reducing their competitiveness in the market.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The tariffs have disrupted established supply chains, prompting eCommerce companies to seek alternative suppliers or consider reshoring production to mitigate costs. However, transitioning supply chains is a complex and time-consuming process, potentially leading to delays and reduced efficiency in order fulfillment.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
With consumer prices potentially rising by 15–20% in certain categories due to the tariffs, shoppers are expected to alter their buying behavior. This shift may include reduced discretionary spending and increased price sensitivity, impacting eCommerce sales volumes. Easyship
Impact on B2B Companies
Business-to-business (B2B) companies are also grappling with the ramifications of the tariffs, affecting various aspects of their operations.
Elevated Production Costs
B2B firms that depend on imported raw materials or components are encountering increased production costs. For example, the aerospace industry is experiencing significant challenges, with companies like Howmet Aerospace declaring “force majeure” due to the tariffs, potentially halting shipments and disrupting production schedules. Reuters
Contractual and Legal Challenges
The sudden imposition of tariffs has led B2B companies to scrutinize existing contracts to assess liability for the additional costs. This legal uncertainty may strain relationships between suppliers and clients, leading to renegotiations or disputes over cost-sharing arrangements. Reuters
Strategic Reevaluation
In response to the tariffs, B2B companies are reevaluating their strategic plans, including exploring nearshoring options to countries with existing free trade agreements, such as those in Central America. This shift aims to reduce tariff exposure and enhance supply chain resilience. Grant Thornton
Curious to Know How to Surf This Wave Through?
Here are 10 top strategies and preparation tips for B2B eCommerce business owners to navigate the uncertain terrain of 2025 and 2026, especially in light of tariff impacts, supply chain instability, and consumer behavior shifts:
Top Strategies for B2B eCommerce Success in 2025–2026
1. Diversify Your Supplier Network
Avoid over-reliance on a single region like China. Build relationships with suppliers across multiple geographies—Southeast Asia, Latin America, or even domestic sources—to mitigate tariff risks and geopolitical disruptions.
2. Nearshore Manufacturing and Warehousing
Move critical production or warehousing closer to your key markets. Nearshoring to countries with free trade agreements (e.g., Mexico or Canada under USMCA) reduces tariff exposure, shortens delivery times, and increases resilience.
3. Conduct a Tariff Impact Audit
Map out which products or components are affected by current and potential tariffs. Understand your cost exposures so you can adjust pricing, contracts, and sourcing strategies in advance.
4. Strengthen Contractual Flexibility
Review and revise supplier and client contracts to include clauses for sudden cost escalations, delivery delays, or force majeure. This reduces the risk of disputes and improves negotiation agility in turbulent times.
5. Automate and Digitize Your Operations
Invest in automation and digital tools to reduce dependency on manual labor and lower operational costs. Tools like ERP, AI-based demand forecasting, and robotic warehouse systems can help offset tariff-related price increases.
6. Optimize Logistics & Inventory Management
Build smarter inventory systems that use real-time data to manage stock levels efficiently. Hold safety stock of critical items, but avoid excess inventory that can become obsolete or costly.
7. Refine Customer Segmentation & Value-Based Pricing
Segment your B2B customers based on profitability, risk exposure, and purchasing volume. Offer tiered pricing models, bundles, or loyalty incentives based on value rather than blanket discounting.
8. Enhance Your eCommerce Tech Stack
Ensure your B2B eCommerce platform supports features like personalized catalogs, customer-specific pricing, bulk ordering, automated invoicing, and real-time inventory syncing to improve buyer experience and reduce churn.
9. Invest in Transparent Communication & Education
B2B buyers expect transparency, especially during times of disruption. Provide regular updates on pricing changes, expected delays, and sourcing decisions. Offer educational content or webinars to strengthen trust.
10. Plan for Scenario-Based Budgeting & Growth
Develop dynamic financial models based on different scenarios—tariff escalation, supply chain failure, or economic slowdown. Align marketing, sales, and procurement budgets accordingly to stay agile.

Here‘s the B2B eCommerce Survival Checklist for 2025–2026:
✅ Diversify suppliers across regions to reduce dependency on China
✅ Nearshore operations to Mexico, Canada, or Central America
✅ Conduct a full tariff impact audit on SKUs and inputs
✅ Update contracts to manage price volatility and legal risks
✅ Automate workflows—ERP, fulfillment, forecasting, and analytics
✅ Streamline inventory with smarter forecasting and safety stock
✅ Personalize pricing and bundling for segmented customers
✅ Upgrade your eCommerce tech stack for B2B-specific needs
✅ Keep clients informed with transparent, proactive communication
✅ Build flexible budgets for multiple economic/tariff scenarios
🛠 The 2025 market crash is a wake-up call. The next 12–24 months will test how well you’ve future-proofed your business.
👉 Which strategy are you focusing on first? Let’s discuss.


Final Thoughts
A New Era of Economic Uncertainty The 2025 U.S. market crash has set the stage for a new era of volatility—fueled by protectionism, geopolitical tension, and inflationary pressures. For investors, businesses, and policymakers alike, the road ahead demands adaptability. Whether it’s recalibrating supply chains in B2B sectors or reshaping pricing models in eCommerce, the winners of tomorrow will be those who act with speed, strategy, and foresight.
Quick Live Update 1: On April 9, 2025, President Donald Trump announced a 90-day suspension of most global tariffs, reducing them to 10%, while simultaneously increasing tariffs on Chinese imports to 125%. This decision came after appeals from over 75 countries and concerns from financial markets. The move led to a significant surge in U.S. stock markets, with the S&P 500 rising 9.5%, the Dow Jones 7.8%, and the Nasdaq over 12%. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent indicated that the pause allows time for tailored trade negotiations with individual nations. Despite this temporary relief, economic uncertainties persist, particularly as trade tensions with China escalate. Critics warn that the policy uncertainty may push the U.S. economy into recession.
Actionable Strategy for the 90-Day Tariff Pause (April 09, 2025 Update)
The 90-day global tariff pause announced by President Trump presents a brief but strategic window for B2B and eCommerce companies to regroup, renegotiate, and realign. While the Chinese tariff hike to 125% remains a threat, the temporary relief for other global trade partners offers a chance to act decisively.
Here’s how to use this short-term breathing space effectively:
✅ 1. Accelerate Supplier Diversification
Use the 90-day window to finalize alternate suppliers in tariff-free or low-tariff regions. Focus especially on Southeast Asia, Latin America, or USMCA countries. Lock in contracts before tariffs potentially return.
✅ 2. Renegotiate Contracts Under Temporary Relief
Leverage reduced tariffs to renegotiate supply or distribution contracts that were previously strained. Emphasize the temporary nature of the pause to create urgency for favorable terms.
✅ 3. Boost Inventory While Costs Are Lower
Stock up on critical imports during the lower tariff period to build buffer inventory. Prioritize high-margin or high-volume SKUs that will be harder to source later.
✅ 4. Launch Tariff-Free Product Promotions
If your business relies heavily on imported goods, create limited-time promotions or “90-Day Relief Discounts” to drive sales while costs are temporarily down—helping improve cash flow and customer acquisition.
✅ 5. Advance Your Nearshoring Decisions
Use this period to pilot or test nearshoring initiatives—whether warehousing in Mexico or working with Central American manufacturers. Gather data, optimize processes, and prepare for long-term transitions.
✅ 6. Monitor Bilateral Trade Talks Closely
Keep a close eye on new country-specific trade negotiations. Countries that secure longer-term exemptions or deals could become new strategic partners—stay ready to pivot sourcing or logistics accordingly.
✅ 7. Revisit Scenario Planning Models
Update your financial and operational models to include the 90-day reprieve. Build “tariff returns” and “exemption continues” scenarios to prepare sales, procurement, and marketing budgets for either outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
The 2025 U.S. Stock Market Crash was primarily caused by aggressive tariff hikes announced by President Donald Trump on April 2, dubbed Liberation Day. These tariffs, especially on Chinese imports (up to 54%), triggered fears of a global trade war, disrupted supply chains, and sent shockwaves through the Nasdaq and other indices, pushing markets into bear territory.
“Liberation Day” refers to April 2, 2025, when the U.S. government implemented sweeping import tariffs. While the name symbolized economic self-reliance, markets interpreted it as a risk to globalization and growth, resulting in the Liberation Day stock market crash.
The Nasdaq bear market 2025 unfolded after the index dropped over 20% from its high, falling from 20,204 to 17,398 in just 32 trading sessions. Big Tech stocks like Tesla, Apple, and Nvidia led the decline due to high exposure to tariffs and Chinese manufacturing.
The Trump tariff impact on the economy included increased input costs, disrupted supply chains, and inflation. The steep tariff hikes—some over 50%—affected consumer prices and business margins, stoking fears of stagflation and recession in Q2 2025.
B2B supply chain disruption became a major concern as companies struggled with higher raw material costs and contract uncertainty. Many reevaluated suppliers, considered nearshoring, and renegotiated terms to minimize losses from sudden tariff changes.
The eCommerce impact of tariffs includes rising product costs, longer delivery times, and changes in consumer behavior. Many online retailers reliant on imports have had to raise prices or shift to alternative sourcing to stay competitive.
Over $6 trillion in market value was wiped out in just two days, making the U.S. Stock Market Crash 2025 one of the most rapid and intense downturns since the dot-com bust. The Dow lost 4,000 points in 48 hours.
Economists and market leaders like Larry Fink have warned the U.S. may already be in a technical recession. Signs include declining GDP forecasts, reduced consumer demand, and inflation triggered by higher import costs.
There’s been a massive tech stock sell-off in 2025. Tesla fell by 43%, Nvidia by 30%, and Apple by 27%. The crash revealed how vulnerable even dominant tech firms are to geopolitical and supply chain risks.
To survive post-crash volatility, businesses must diversify suppliers, automate operations, reevaluate pricing models, and invest in scenario planning. Our full 2025–2026 B2B survival checklist outlines 10 key strategies.








































